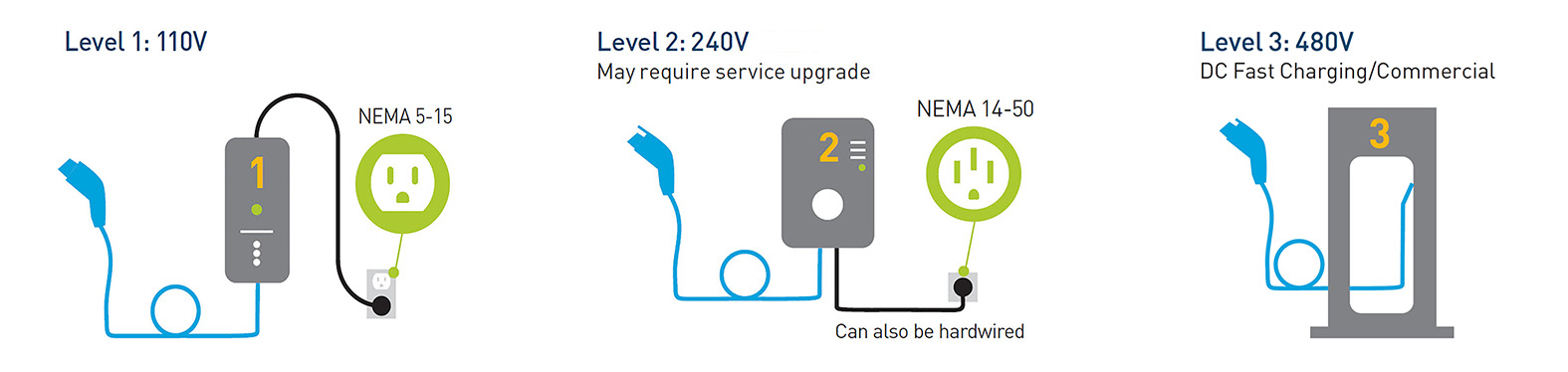
Good for: Battery EVs
Miles/charge time: 13 to 25 miles per hour of charge
Voltage: 240V
Level 2 charging stations are four times faster than Level 1 and can provide about 25 miles per hour of charge.
Level 2 stations require a professionally installed 240-volt outlet on a dedicated circuit. If you’d like one installed in your home, contact a licensed electrician to get an estimate and to determine if a permit is required.
Level 2 might be the right choice if you drive a battery EV, as these cars have larger batteries that require longer charging times. Drivers with longer commutes or who want a faster charge or a longer electric driving range should also consider choosing a Level 2 charging station.
Level 2 purchasing considerations
On average, the cost of a Level 2 charging station ranges from $500 - $700. A charger may cost more or less depending on key features such as portability, amperage, and WiFi capability.
Choosing Amps
To determine how much power will flow to your car, multiply the Volts by the Amps and divide by 1,000 (Amps x Volts/1,000). For example, a 240-V Level 2 charging station with a 30-amp rating will supply 7.2 kW (30 x 240 /1,000). After one hour of charging, your EV will add 7.2kW X 1 hr = 7.2 kWh of energy to your vehicle.
To calculate how long it will take to charge the entire capacity of the battery, refer to the manufacturer's documents to determine the battery capacity of your EV.
Example based on an all-electric model:
- EV battery capacity – 42kWh
- EV charger energy delivery – 7.2kW
- Total hours to charge = EV battery capacity / EV charger energy delivery = hours
- 42kWh / 7.2kW = 5.83 hours
Americans drive around 30 miles per day. If you want more than 50 miles of range from overnight charging, you will need a station with at least 16 amps. Level 2 residential chargers range from 16 to 80 amps.
Charging times, range, and size of battery vary by vehicle.
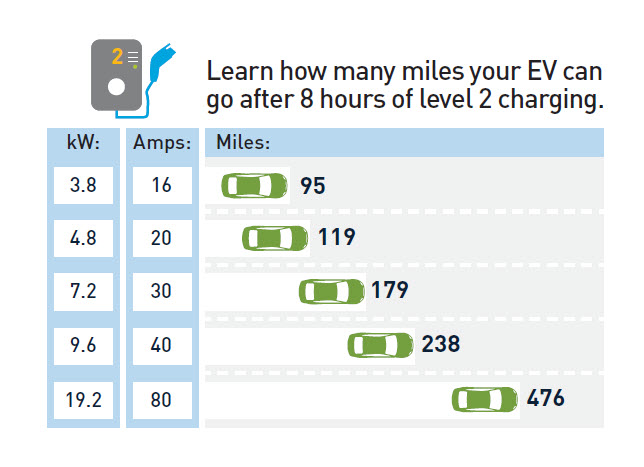
The chart above assumes:
- Chargers are operating on a 240-volt outlet.
- Your vehicle travels 3.1 miles per kilowatt-hour.
Use the PG&E Energy Action Guide to search and compare Level 2 residential charging stations from a range of retailers. You can also read customer reviews and purchase chargers directly from retailers.
Visit the PG&E Energy Action Guide
Consider portability
Decide if you want a hard-wired and permanently-mounted charger, or a portable unit that simply plugs into a 240-volt outlet and will hang on the wall. Portable chargers allow you to take the charger with you if you move.
Cord length
Determine where your charger will be located. Note that the further the charger is from your home's utility panel, the more costly the installation. Measure the distance from where your car will be parked to your charger location to determine the required cable length. Cables range from 12 to 25 feet.
Smart connectivity
Smart chargers connect to your WiFi and allow you to program charging from your phone and monitor your charging habits. However, most EV drivers now have the ability to control charging through their car's own app.
Level 2 installation checklist
Get help with choosing and installing the right charging station for your home. View the charger installation checklist (PDF).
- The average cost for installing a Level 2 charging station ranges from $400 to $1,200 excluding charger cost.
- Installation costs will vary depending on electrical upgrades, cable length, and other features identified below.
Steps to guide your installation
Step 1: Get an electrical assessment of your home.
Talk with a qualified electrician to assess whether your electrical panel has the capacity for a Level 2 charger.
- Upgrades and permits at your expense may be necessary.
- The EV manufacturer may also offer a home assessment as part of your purchase.
- The electrician can also install a dedicated 240-volt circuit (similar outlet used for an electric clothes dryer) to serve the Level 2 charger if your panel does not have the necessary capacity.
Be sure to discuss the following when consulting with an electrician.
- Upgrades to your electrical panel
- Desired location of charger
- Cost of installation
- Length of charging cord
- Type of charger you have or want
- Permitting and inspections (if required by your city)
- Timeline for job completion
Step 2: Determine which electric rate and meter system works for you.
Select the PG&E electric rate that is best for your charging needs. You can enroll in any residential rate. The EV2-A rate plan works for customers who have an electric vehicle (EV) and/or battery storage and can charge during off-peak hours of 12 a.m. to 3 p.m., in addition to shifting other household energy usage to off-peak hours. The EV-B rate may be useful for people who want to have one electric rate for their whole house and a separate EV rate for their electric car charging.
Find out which rate is the best fit for you here: EV Savings Calculator.
- Single existing meter: You can enroll in EV2-A, E-ELEC, E-1, E-TOUC, or E-TOUD rates.
- Dual meter: If you want to install a second meter and electric panel for EV charging, you'll enroll in the EV-B rate.
 Note: PG&E representative may schedule a visit to determine whether your current electric service can support an EV. You may have to upgrade your service or your panel or add a second electric panel. Service upgrades are necessary when the service wire to your home does not meet your capacity needs. PG&E charges a $100 service fee for a second meter. You’re responsible for the installation costs to support an additional meter. The costs are generally around $2,000, but can be as high as $8,000 or more.
Note: PG&E representative may schedule a visit to determine whether your current electric service can support an EV. You may have to upgrade your service or your panel or add a second electric panel. Service upgrades are necessary when the service wire to your home does not meet your capacity needs. PG&E charges a $100 service fee for a second meter. You’re responsible for the installation costs to support an additional meter. The costs are generally around $2,000, but can be as high as $8,000 or more.
Step 3: Contact PG&E to start your "change of service" application
After you determine which EV charging system is right for you, contact PG&E. You must complete an application to notify PG&E of the change of service including the following information:
- Rate option: Choose the residential rate you'll use to charge your EV.
- Charging level: Will you use a Level 1 or Level 2 charging station.
- Charging load: Load amount from your EV supply equipment. This is based on the charging system's voltage and amperage. An electrician can help you determine this information.
- Panel upgrade: Does the dedicated circuit require a panel upgrade?
Two ways to apply: